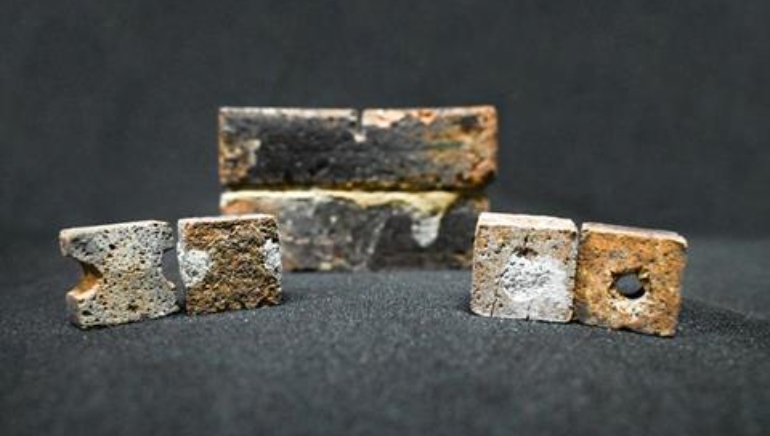
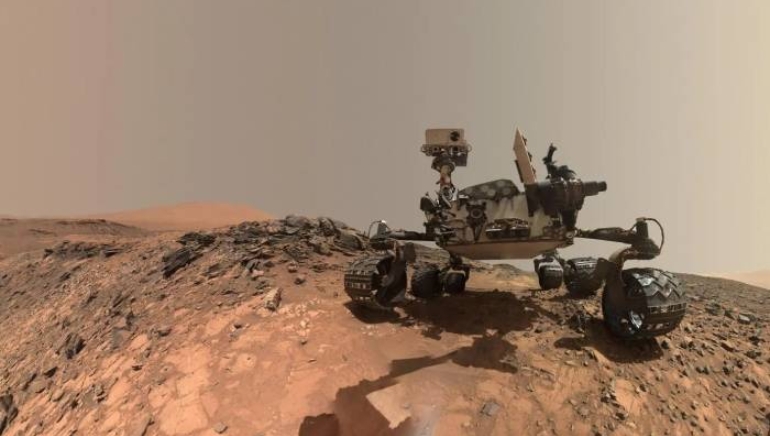
Scientists at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) developed an innovative bacteria-based process for repairing space bricks, a critical step in lunar colony construction. This breakthrough technology addresses the structural damage caused by high-temperature changes on the moon.
The research aligns with global attempts to construct permanent human settlements on the moon, particularly through NASA’s Artemis program. Traditionally, space missions have relied on bringing building materials from Earth, which is both costly and logistically demanding. However, the IISc team has developed an alternative that combines lunar soil, known as regolith, with Sporosarcina pasteurii, a bacterium that can convert urea and calcium into calcium carbonate. This natural binding agent hardens soil particles, resulting in strong, brick-like structures.
Moon temperatures range from 121°C to -133 °C, causing cracks in construction materials. To address this issue, researchers devised a restoration procedure in which a slurry of S. pasteurii, guar gum, and lunar soil simulant is injected into injured areas. The bacteria make calcium carbonate, which effectively fills cracks and strengthens the structure.
Encouraged by successful experiments, IISc researchers propose testing S. pasteurii in orbit as part of India’s Gaganyaan expedition. Understanding bacterial behaviour in microgravity may open up new avenues for sustainable extraterrestrial construction, lowering reliance on Earth-sourced materials.