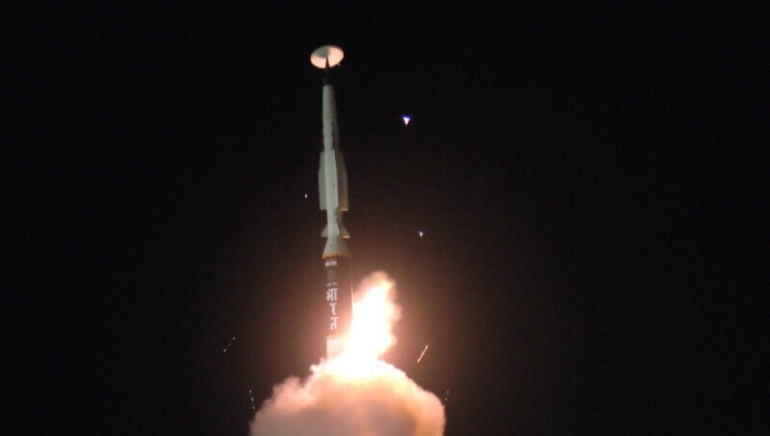
India has attained one of the key milestones in military development, putting itself as one of the listers in small groups of nations progressing towards advanced technology. The nation has successfully tested a domestically developed long-range hypersonic missile on Sunday. Alongside China, Russia, and the United States, India is trying to put up with the development of advanced long-range missiles as a result of the global push for hypersonic weapon figures.
The state-run Defence Research and Development Organisation developed the missile alongside other industry partners to carry payloads for ranges. As stated in a statement, this exceeds 1500 hm for the government and armed forces.
They said, “The flight data … confirmed the successful terminal maneuvers and impact with a high degree of accuracy.” As per the claims put out by the team, the first test-firing took place on Saturday from Dr APJ Abdul Kalam island off the eastern coast of Odisha.
As per Rajnath Singh, the defense minister, the test is a “historic achievement.” He mentioned this through a post on X, adding that India is amongst a few selected groups of nations to process such critical and advanced technologies.