On the occasion of World Refugee Day, more than 40 corporations, including Louis Vuitton, Adidas, Starbucks, L’Oreal, PepsiCo, and Hyatt have pledged to hire, connect to work, or train a total of 2,50,000 refugees in Europe, with 13,680 of them getting jobs directly in those companies.
World Refugee Day is celebrated on June 20 every year. The day is designated by the United Nations to honour refugees from around the world.
Companies such as Amazon Inc, Marriott International, and Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc have pledged to hire refugees, especially women who fled war-torn Ukraine, in a hope to fill staffing needs after the economy bounced back from the COVID-19 pandemic. A severe economic crisis, the pandemic also led to challenges like violence, war, poverty, and refugee crisis.
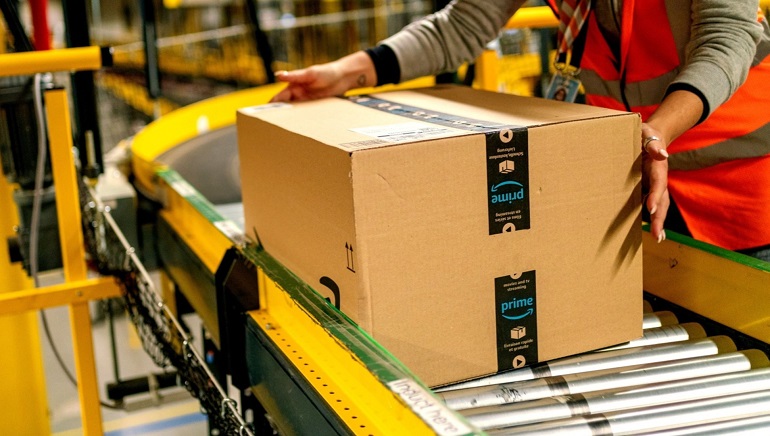
Amazon will hire at least 5,000 refugees over the next three years in Europe, followed by Marriott and Hilton with 1,500 each, Starbucks and ISS with 1,000 each. Brands like Adidas, Starbucks, L’Oreal, PepsiCo, and Hyatt have smaller commitments. Amazon has said that the vast majority of jobs will be hourly roles at fulfilment and storage centres and in transport and delivery. Jobs offered by Marriott will be hourly positions such as housekeepers, kitchen staff and front desk attendants.
According to the United Nations, 110 million people have been displaced worldwide, with about 12 million from Ukraine, nearly half of whom are living in Europe after the continent’s largest movement of refugees since World War II.