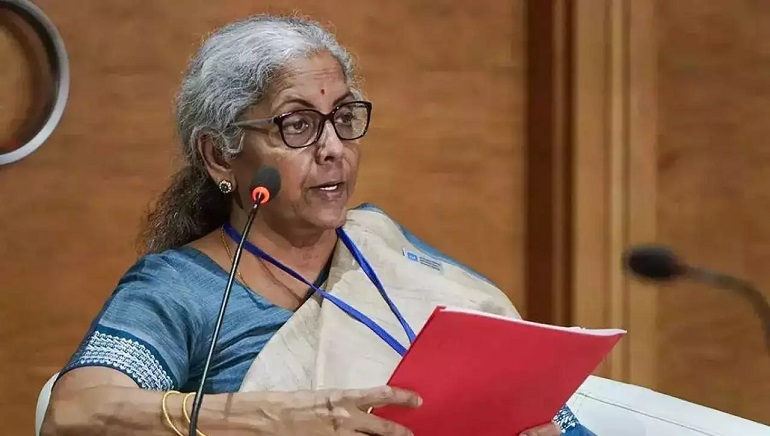
The Indian economy today is transparent, open and watchable, said Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman while addressing the US business community on April 11 in Washington, encouraging them to come and invest in India and be part of the country’s amazing growth story.
The union minister was speaking at a luncheon meeting of the US-India Strategic and Partnership Forum, where she told representatives of the top US companies that the current state of the Indian economy is due to the path-breaking and futuristic reforms, such as digitisation, undertaken by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in the last nine years.
She added that for the next 25 years in the budget, the government has proposed that India should become an artificial intelligence (AI) hub. Three centres of excellence have been proposed in the premier institutions such as the Indian Institute of Technology, which would research into AI and find out tools that can make the life of businesses or householders easy.
Nirmala Sitharaman’s pitch to the US business community also highlighted the government’s hydrogen mission announced in the last two budgets. The Indian government has specifically identified the next 25 years leading towards India’s hundred years of being free from Imperial rule, added the minister. “So, by 2047, we expect India…meeting the aspirations of our youth…You’re looking at a very high potentially youthful, very skilled population which is going to contribute to India’s growth,” Sitharaman said.