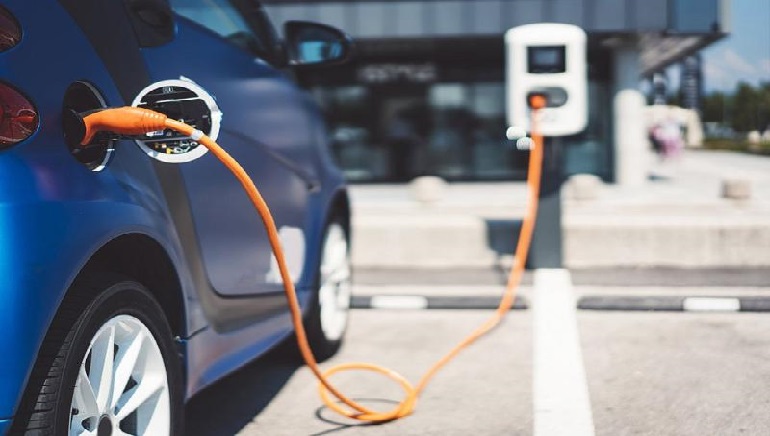
In an attempt to reduce or end CO2 emissions, the 27-member European Union approved and announced its plan early Wednesday to end the sale of combustion engine vehicles by 2035.
The step put forward in July 2021 will put an end to sales of petrol and diesel cars and also light commercial vehicles, entirely shifting to electric engines in the European Union from 2035.
The plan is meant to help fulfill Europe’s climate objectives, mostly carbon neutrality by 2050.
The plea of countries including Germany and Italy, the EU-27 also accepted to contemplate a future green light for the use of replacement technologies such as synthetic fuels or plug-in hybrids
While the agreement is intended to achieve the complete elimination of greenhouse gas emissions, environmental NGOs have opposed the technologies.
French Minister of Ecological Transition Agnes Pannier-Runacher, who chaired Tuesday night’s meeting said, “This is an enormous challenge for our automotive industry” She also said these decisions would “allow a planned and accompanied transition”
The continent’s automotive industry, which is already making tremendous investments in the move to electric vehicles, fears the social impact of a rapid change.
At a press conference, Frans Timmermans, the EU Commission Vice President in charge of the European Green Deal, said “The overwhelming majority of car manufacturers have chosen electric cars”.